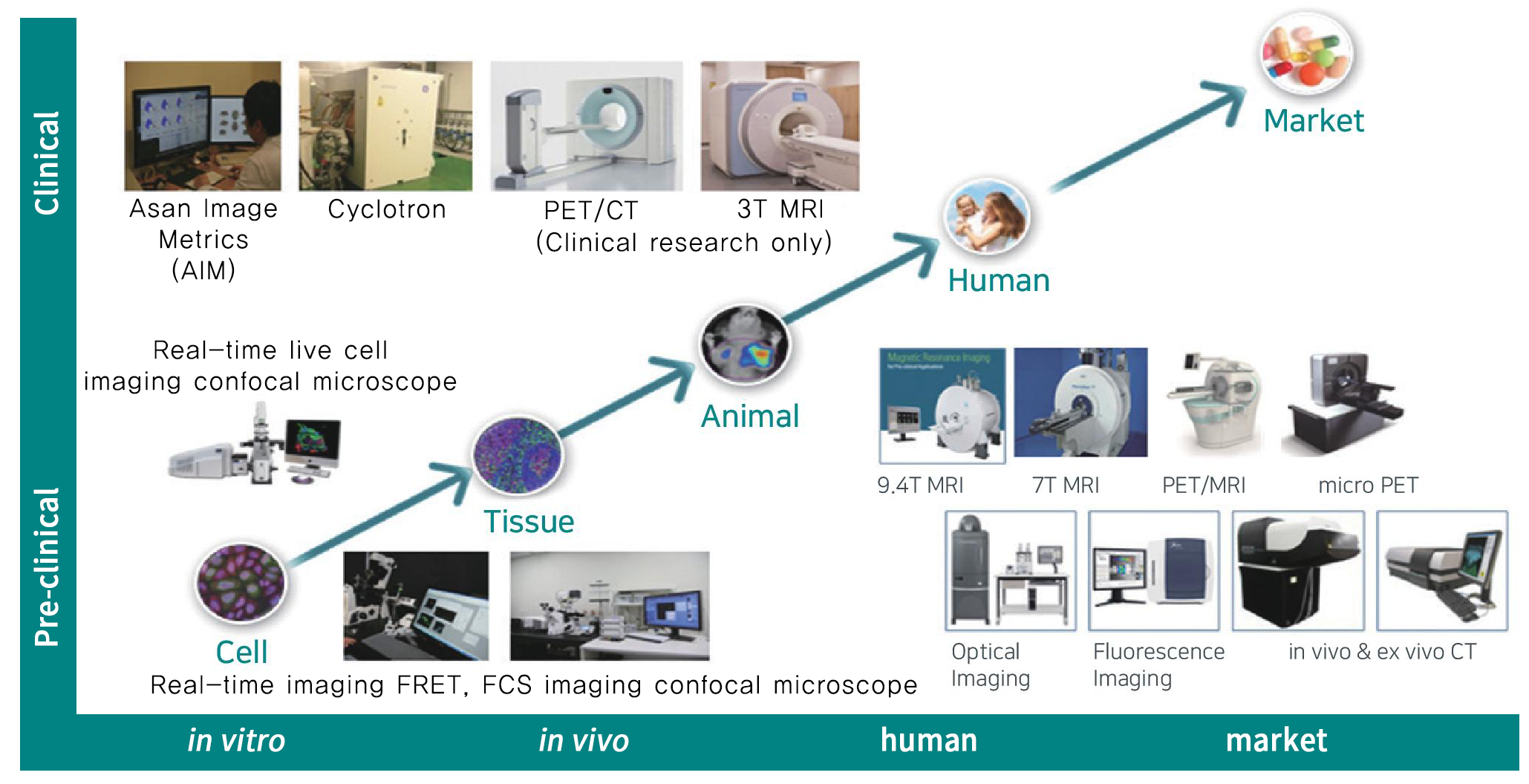
Equipment and techniques
* Radiopharmaceuticals marked with an asterisk (*) require thorough prior discussion with the PET core facility to determine feasibility and scheduling before proceeding.
|
Type of Imaging |
Classification |
Target/Mechanism |
|
Optical Imaging (Monitoring treatment response and measurement of size) |
Evaluation of cancer metastasis and therapeutic efficacy using bioluminescence imaging |
|
|
Drug efficacy assessment through apoptosis imaging |
||
|
Nuclear medicine imaging, PET (Functional or metabolic assessment of tumor) |
[18F]FDG | Glucose metabolism |
| [18F]FLT * | DNA replication | |
| [18F]FMISO * | Hypoxia | |
| [18F]FES * | Estrogen receptor | |
| [18F]FDOPA/[18F]FET * | Amino acid metabolism | |
| [68Ga]DOTATOC | Somatostatin receptor | |
|
Magnetic resonance imaging, MRI (Size measurement and functional assessment of tumor) |
T1w/T2w/PD | Lesion imaging of Solid tumor, Measurement of T1/T2/T2* mapping-Volume |
| DWI |
Diffusion weighted imaging, Tissue/Cellularity measurement |
|
| DCE, DSC, FAIR | Dynamic Contrast Enhanced, Dynamic Susceptibility Contrast (DSC) perfusion imaging (Angiogenetic imaging) | |
| 1H MR spectroscopy | Metabolic imaging | |
Service
- Customized study design
- in vitro / in vivo / ex vivo imaging
- Tumor growth inhibition (TGI) experiments
- Mechanism of action (MOA) and proof-of-concept (POC) validation
- Pharmacodynamic (PD) / pharmacokinetic (PK) assessment using fluorescence imaging techniques
- Immunoprofiling
- Tumor microenvironment assessment via multiplex IHC
Service example (Tumor tracking using imaging)

- Animal : Mouse
[Chemical induced hepatocellular carcinoma] - 9.4T MRI[Acial, T2w Images]
- Monitoring for 5 months (Tumor growth]
Liver cancer imaging using MRI

[18F]FDG, MC38 model

Before treatment

After treatment
Optical imaging of metastatic lung cancer





